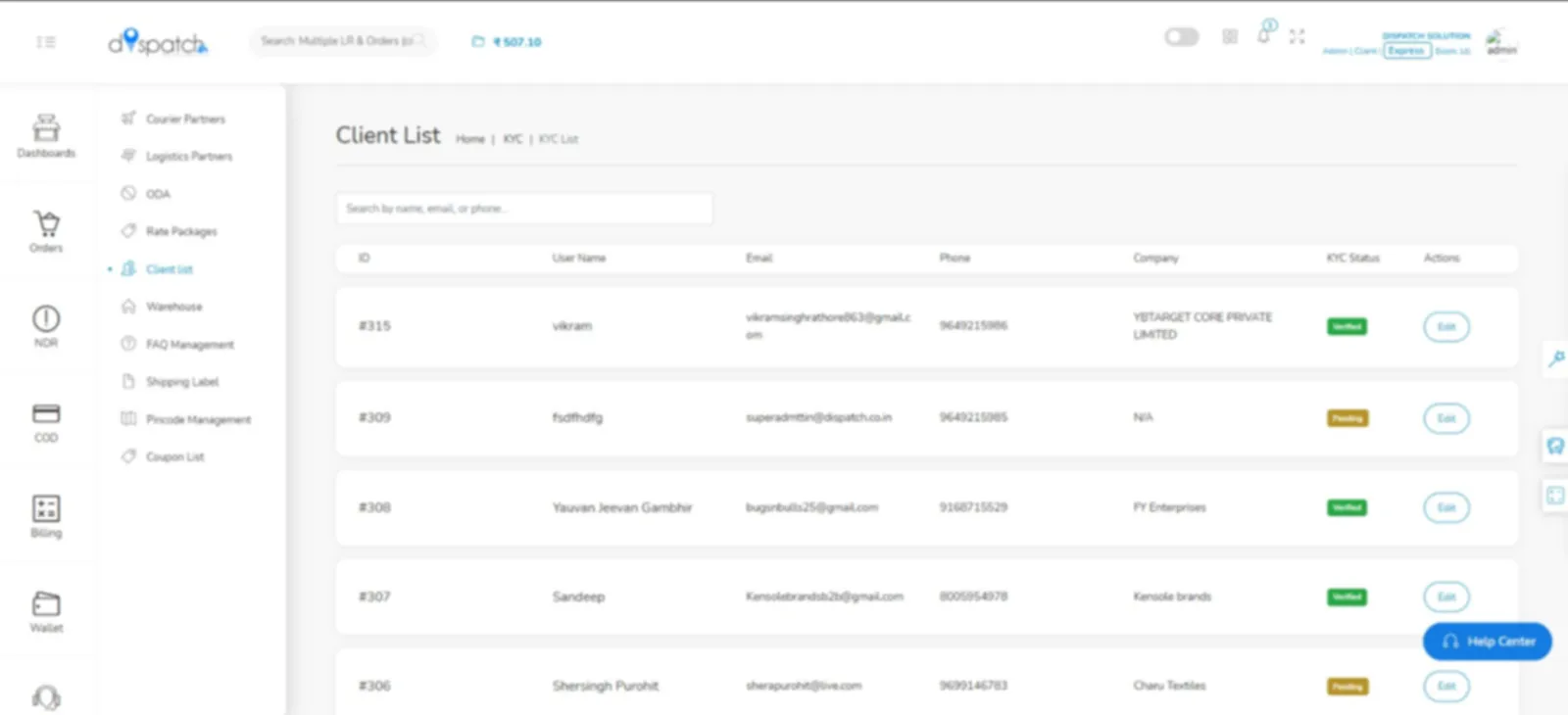
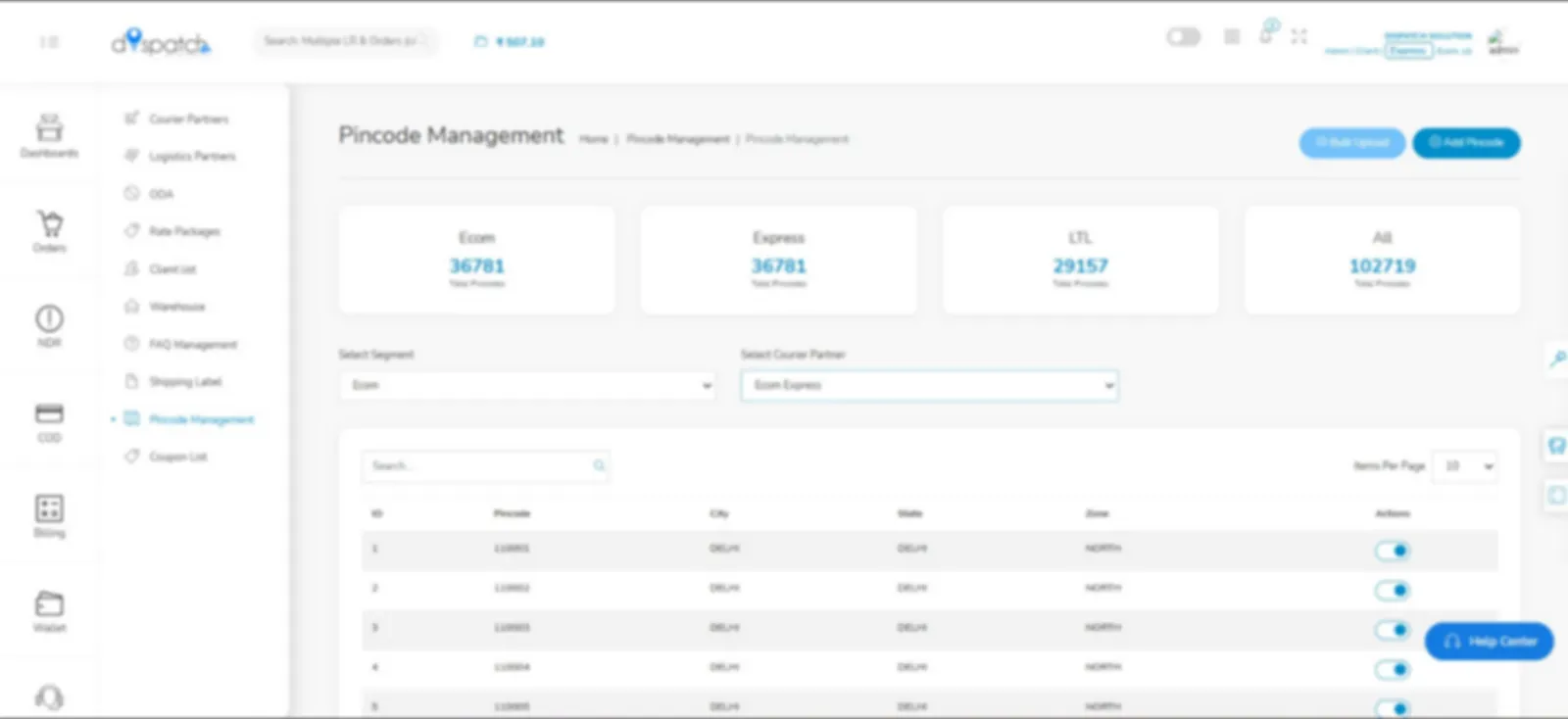
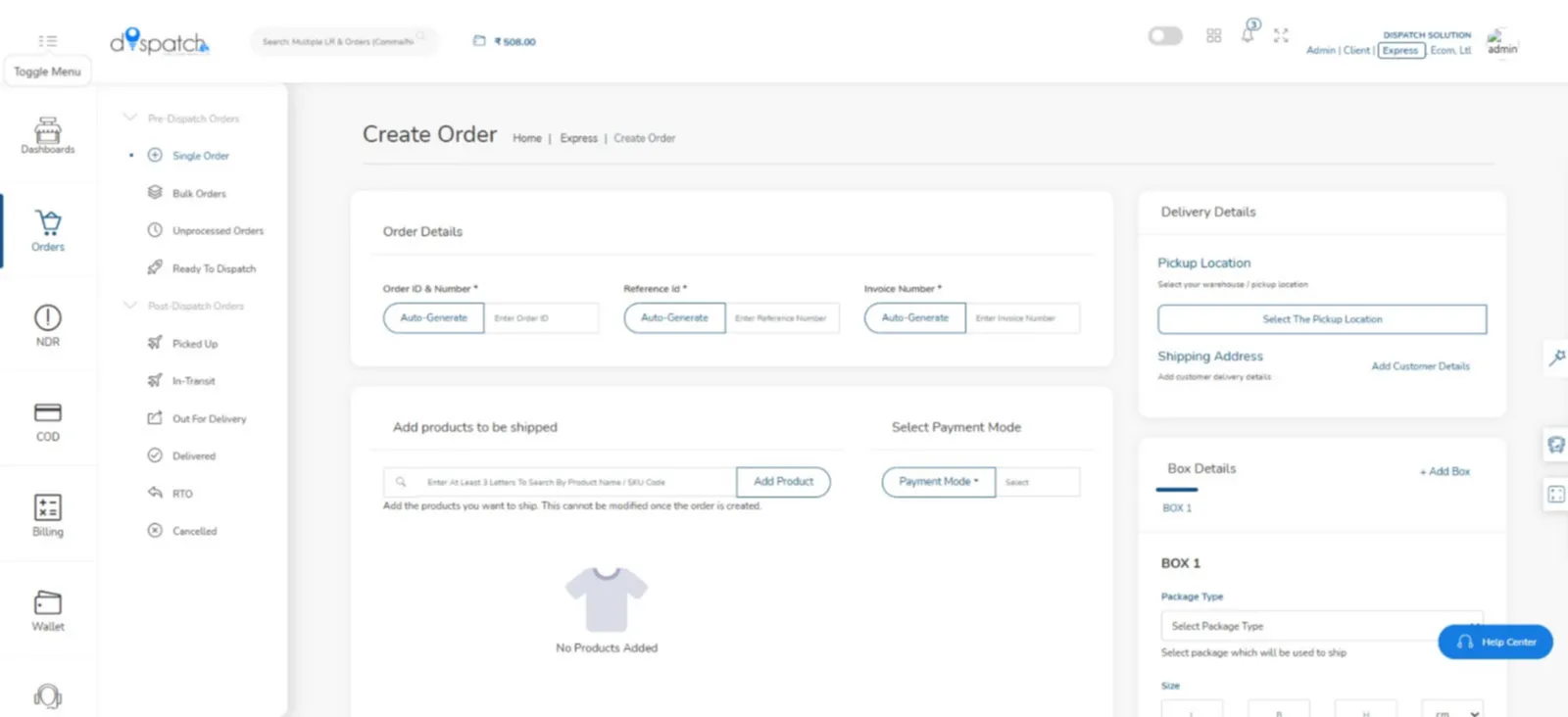
One Platform — Seamless Shipping with Same-Day & Next-Day Delivery Across Domestic & International
Same-Day & Next-Day Logistics Services — Fast, Reliable & Domestic & International Delivery
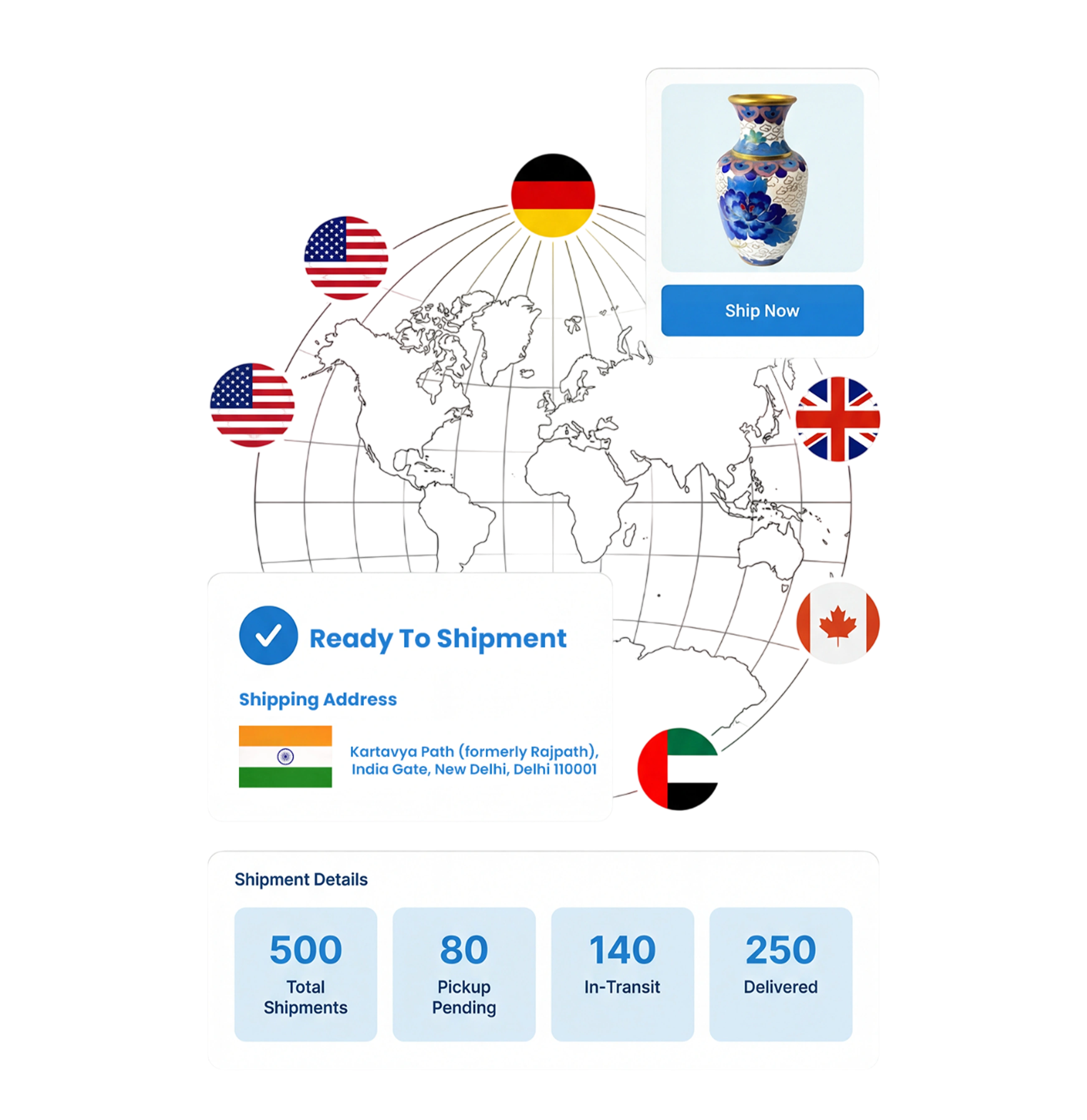
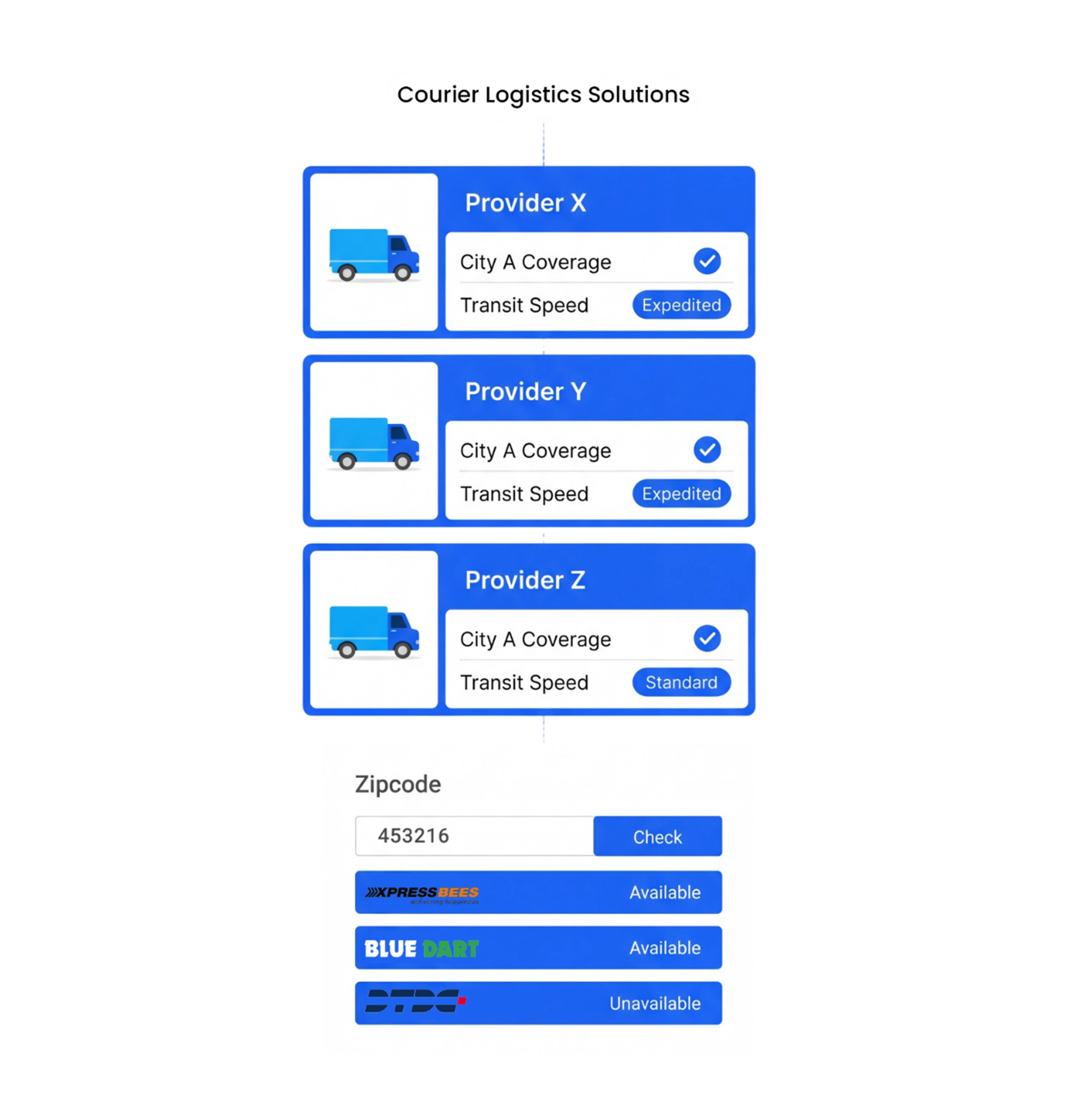
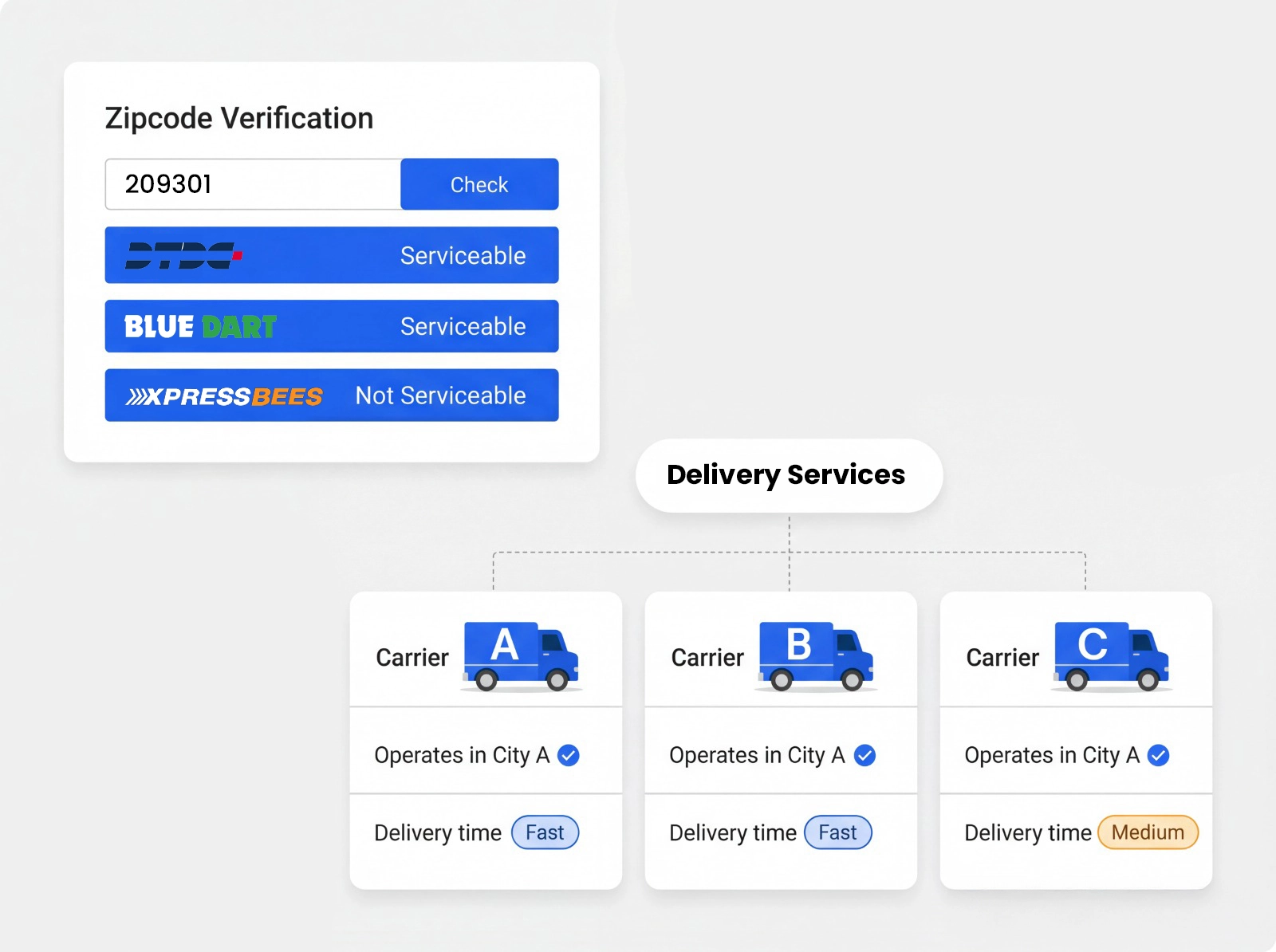
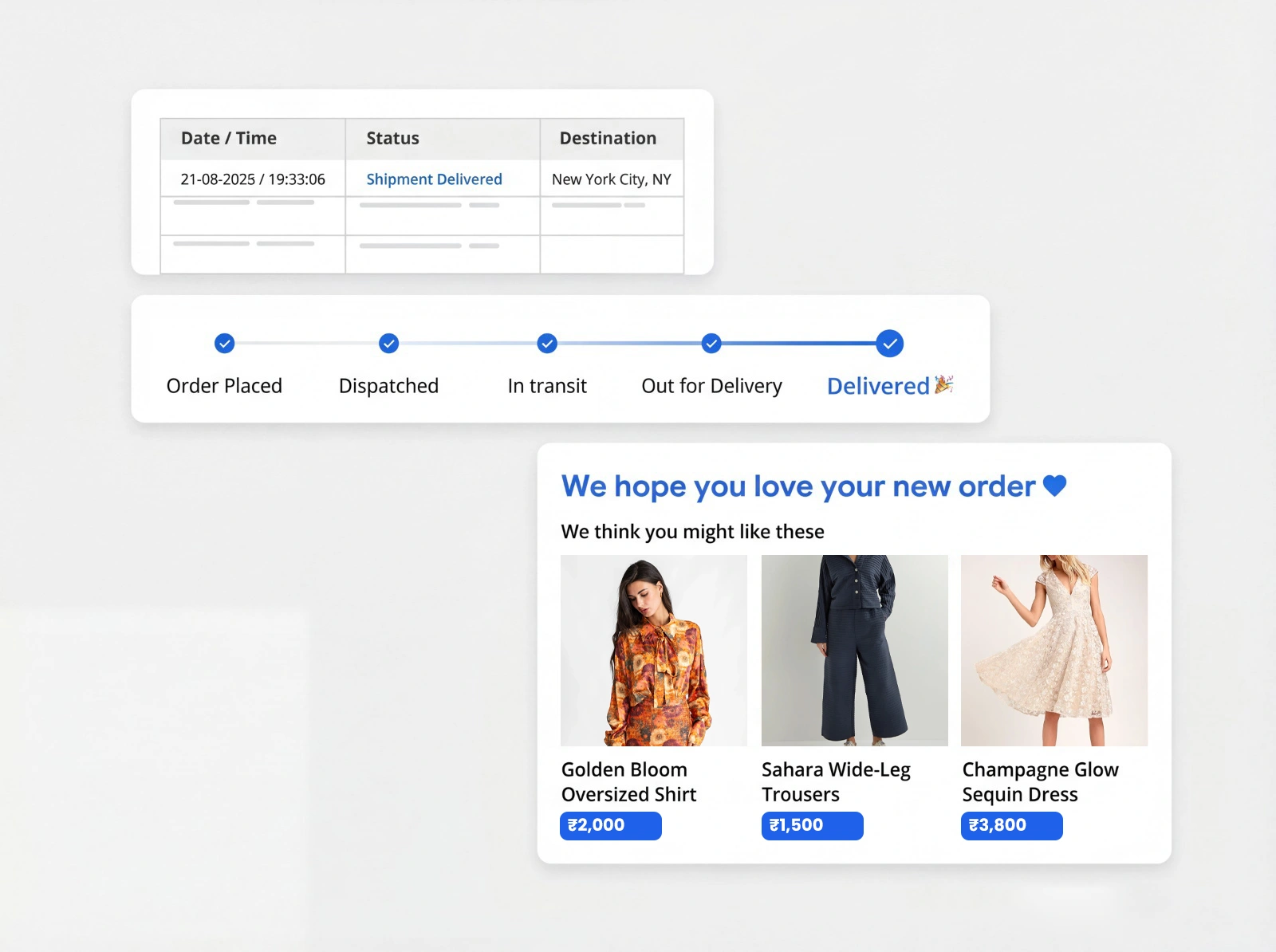
B2B & B2C Shipping Solutions with Real-Time Tracking & Same/ Next-Day Delivery Domestic & International
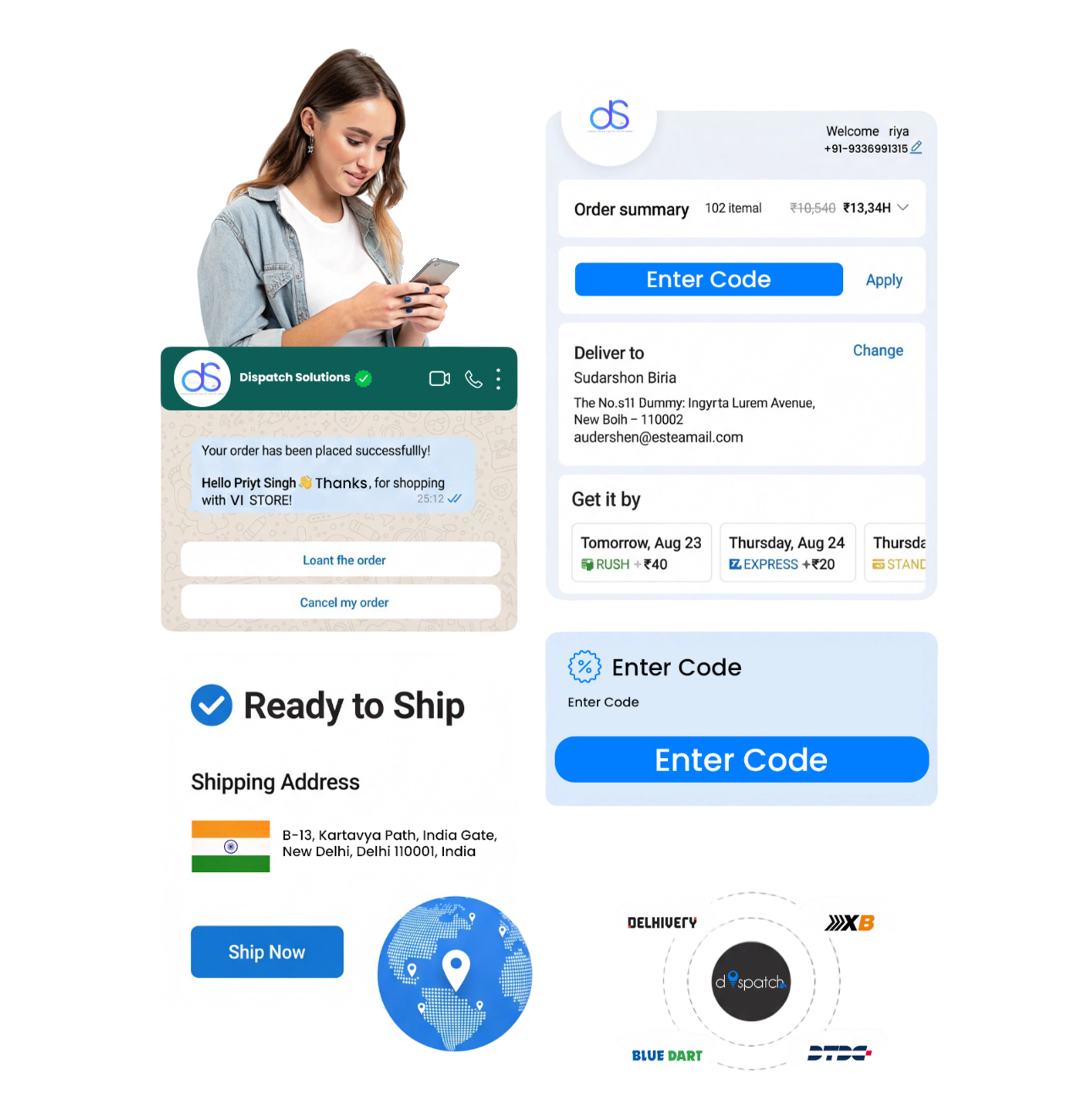
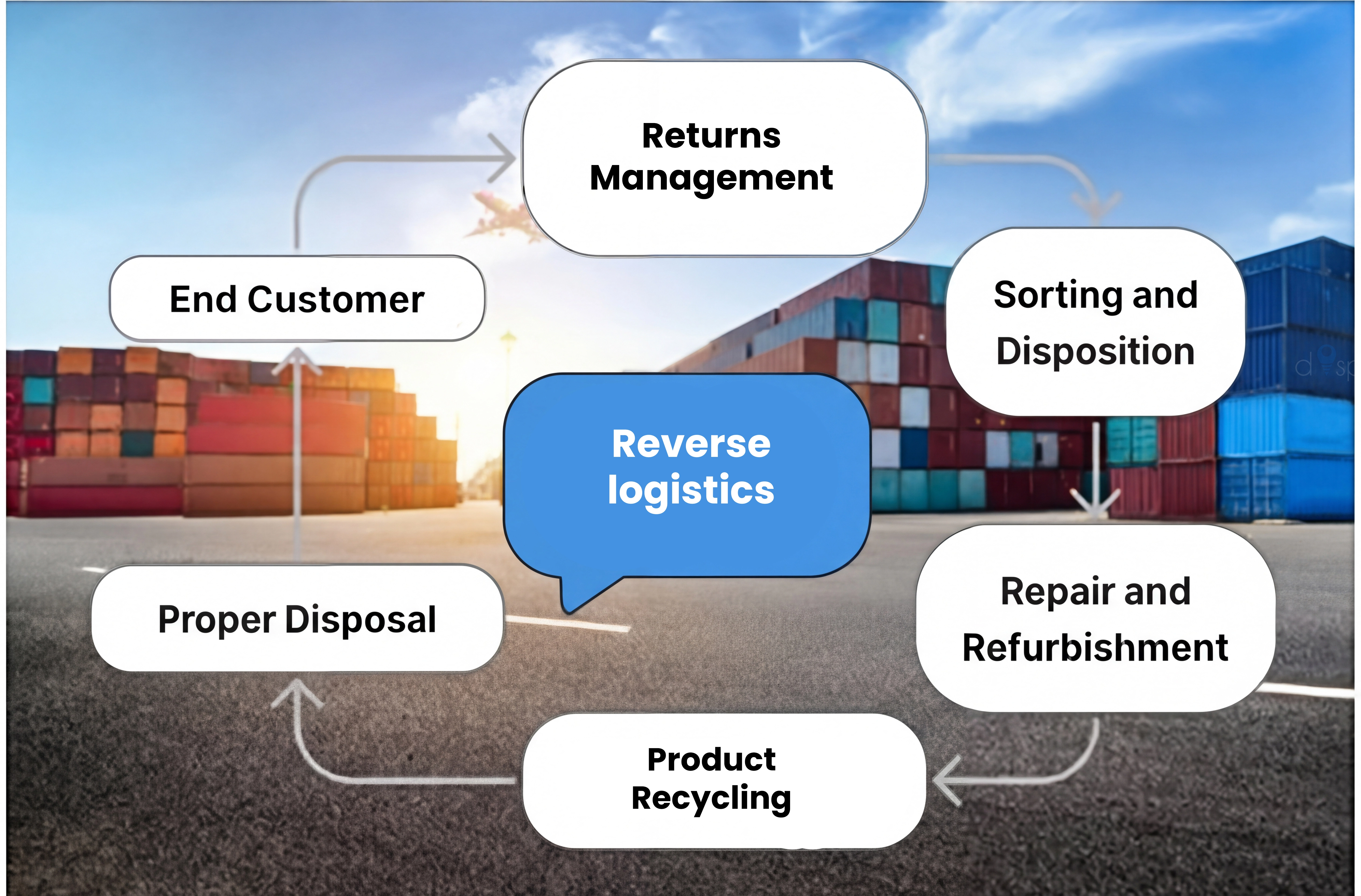
Your Trusted Partner for Same-Day & Next-Day Ecommerce Fulfillment & Logistics
Optimize your deliveries with Same-Day & Next-Day shipping — secure, efficient and on-time across Domestic & International Delivery.
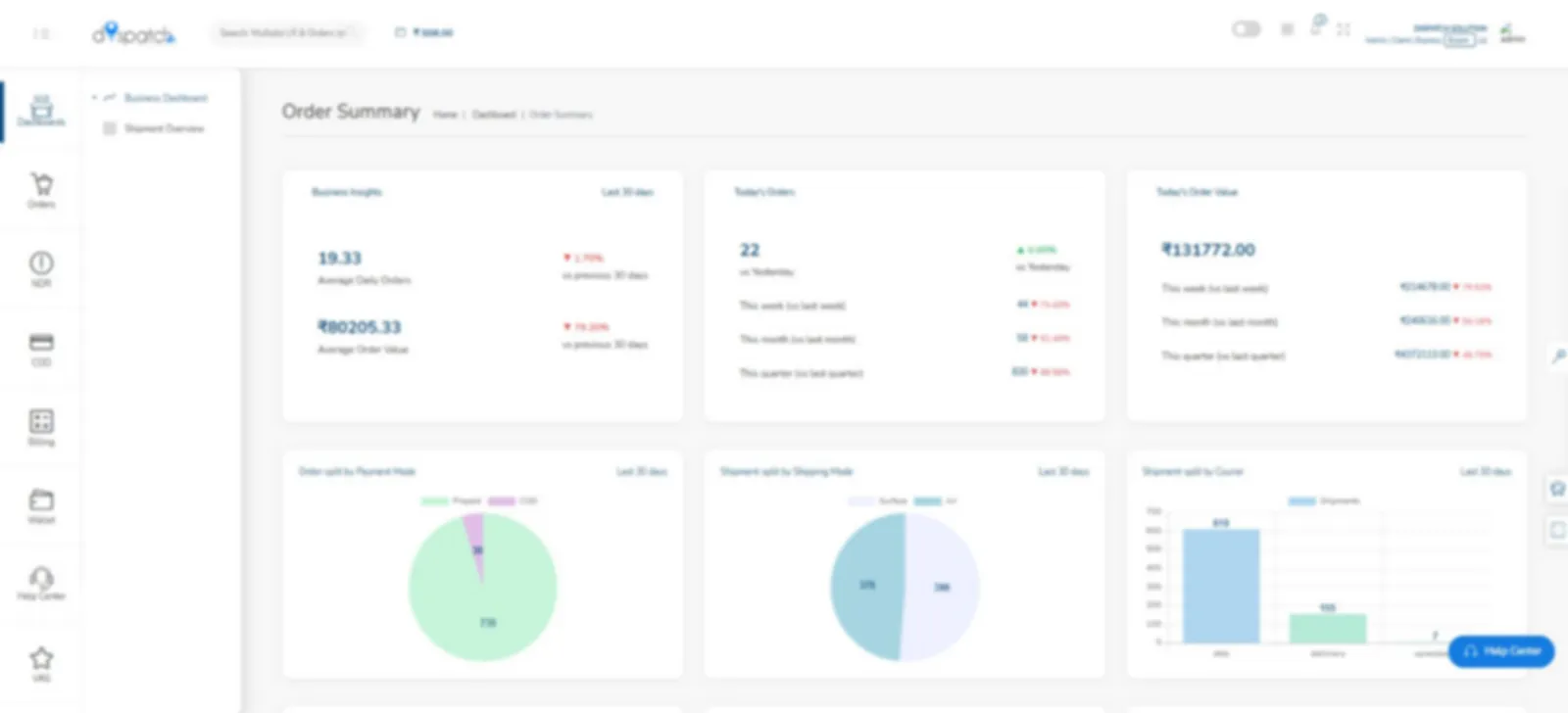
Advanced technology, real-time tracking and assured Same-Day & Next-Day logistics performance for every shipment.
Transparent pricing, dedicated support and reliable Same-Day & Next-Day courier services for growing businesses.
Join leading brands across Domestic & International who trust Dispatch Solutions for Same-Day & Next-Day ecommerce shipping.
Get Started Now